Solid State
Solids are the chemical substances which
are characterised by
define shape and volume, rigidity, high density, low compressibility. The
constituent particles (atoms, molecules or ions) are closely packed and held together
by strong interparticle forces

Characteristic
properties of the solid state:
Ø They
have definite mass, volume and shape.
Ø Intermolecular
distances are short.
Ø Intermolecular
forces are strong.
Ø Their
constituent particles (atoms, molecules or ions) have fixed positions and can
only oscillate about their mean positions.
Ø They
are incompressible and rigid.
Cause of Existence of Solid State
The solid state exists because of following reasons. They are:
·
Intermolecular Forces
·
Thermal Energy
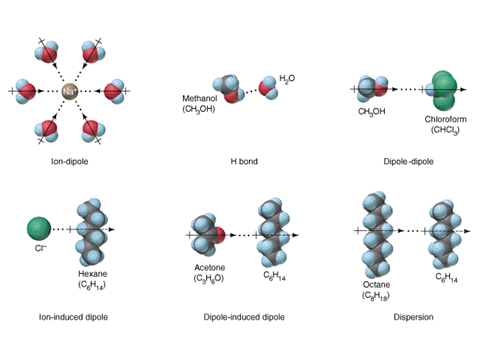
Intermolecular Forces
The forces between constituent particles of matter inside solid
are known as intermolecular forces. The forces are attractive in nature and are
responsible for holding all the particles together and making the existence of
solid state possible. The constituent particles are held such that they can’t
move from their position and adhere to only oscillate about their mean
position. There are four types of intermolecular forces, namely:
·
Dipole-Dipole forces
·
London Dispersion
forces
·
Hydrogen bonding
·
Induced-dipole forces
All the first three intermolecular forces are collectively
called Van der Waals Forces and are responsible for the existence of
solid.
Thermal Energy
The energy acting between constituent particles of matter in a
solid is known as Thermal Energy. Thermal energy is also called Kinetic
Energyand
is responsible for motion of molecules inside solid lattice. Thermal energy
increases with increase in temperature. And hence more the thermal energy
faster will be the movement of molecules. At low temperature the value of
thermal energy is low and intermolecular forces are stronger. This resists the
flow of molecules and adhere them to oscillate about their mean position.