Polyhalogen Compounds
Uses and environment effects
Dihalogen Derivatives
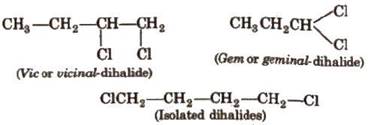
In
this reaction simple Halogenation of alkenes is done to get dihalogenated
compounds
Dichloromethane (CH2Cl2) is
widely used as a solvent, as a propellant in aerosols. Direct contact of
dichloromethane in humans causes intense burning and milk redness of the skin.
Trihalogen Derivatives
1.
Chloroform [Trichloromethane,
CHCl3]
Methods
of preparation
![]()
Haloform Reaction
![]()
![]() [Chlorination]
[Chlorination]
![]()
Properties
1. Oxidation of CHCl3 gives poisonous gas phosgene (carbonyl
chloride).
![]()
phosgene
To avoid this oxidation CHCl3 is stored in dark brown bottles
and filled to the brim. 1% ethanol is added to chloroform which converts
harmful phosgene gas into diethyl carbonate.
2. CHCl3 is widely used in the
production of freon refrigerant R-22.
3. On nitration, it gives tear producing insecticide
substance chloropicrin. It follows free radical mechanism.
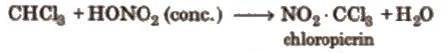
4. On dehalogenation, it gives C2H2 (acetylene)
![]()
5. When subjected to hydrolysis, it gives formate.
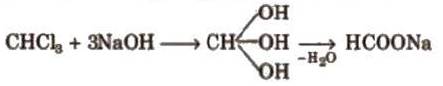
2.
Iodoform (tri-iodornethane,
CHl3)
Iodoform is prepared by iodoform reaction.
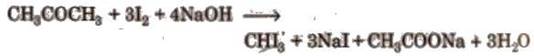
Compounds containing either
CH3CO-
or CH3CH(OH) group form yellow colour iodoform with I2 and
NaOH.
Iodoform when comes in contact with
organic matter, decomposes easily to free iodine, an antiseptic. Due to its
objectionable smell, it has been replaced by other formulations containing
iodine.
Polyhalogen Derivatives
1.
Tetrachloromethane (Carbon Tetrachloride, CCl4)
Preparation
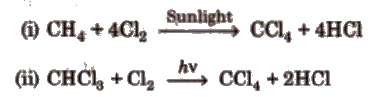
In Methane
gas initially Chlorine is added via free radical mechanism due to action of
sunlight and thus Carbon Tetrachloride is formed. This done by taking methane
gas in chlorine gas atmosphere in presence of sunlight.
Sometimes if
Chloroform is available then also by same mechanism carbon tetra chloride is
made by taking less amount chlorine.
CCI4 is a colourless,
non-inflammable, poisonous liquid, soluble in alcohol and ether.
Carbon tetrachloride is used
1. as a solvent
for oils, fats, resins
2. in dry
cleaning
3. as fire extinguisher under the name ‘pyrene’.
2.
Freons
The chlorofluorocarbon
compounds of methane and ethane are collectively known as freons.
These are usually produced for aerosol propellants, refrigeration and air
conditioning purposes. Carbon tetra chloride when reacts with antimony trifluoride in the presence of SbCl5 as catalyst, dichlorofluromethane
(freon) is obtained.
3.
DDT (p, p’-Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane)
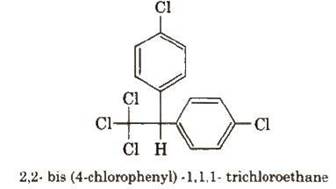
DDT is the first chlorinated
organic insecticide. Its stability and fat solubility’is
a great problem.
It is prepared from chloral and chlorobenzene in the presence
of conc. H2SO4·
4.
Perchloroethane (C2Cl6)
It is used as moth repellant and is also known as artificial camphor.