Solutions
Solutions
Solutions are homogeneous mixtures of two or more than two
components
Solvents
Generally, the component that is present in the largest
quantity is known as solvent. Solvent determines the physical state in which
solution exists.
Solute
One or more components present in the solution other than
solvent are called solutes.
Types of
solutions
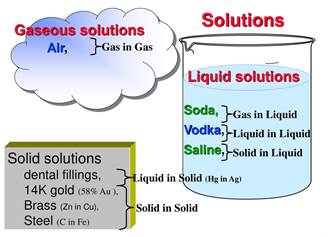
Gaseous solution
If the solvent
is a gas, then it is gaseous solution. An example of a gaseous
solution is air (oxygen and other gases dissolved in nitrogen).
Liquid solution
A liquid solution is a homogeneous solution that is
comprised of a solvent and a solute (there can be multiple solutes in the
solvent). The resulting solution is completely liquid, meaning there is no
precipitated material throughout the solution. Even though it is liquid in
composition, you can have both solids and gases in the solution.
An example would be having a glass of water (H2O)
and adding a little salt (NaCl).
Solid solution
A solid
solution is a solid-state solution of
one or more solutes in a solvent. Such a multi-component system is
considered a solution rather than a compound when
the crystal structure of the solvent
remains unchanged by addition of the solutes, and when the chemical components
remain in a single homogeneous phase.
|
Type
of Solution |
Solute |
Solvent |
Common
Examples |
|
Gaseous
Solutions |
Gas |
Gas |
Mixture
of oxygen and nitrogen gases |
|
Liquid |
Gas |
Chloroform
mixed with nitrogen gas |
|
|
Solid |
Gas |
Camphor
in nitrogen gas |
|
|
Liquid solutions |
Gas |
Liquid |
Oxygen
dissolved in water |
|
Liquid |
Liquid |
Ethanol
dissolved in water |
|
|
Solid |
Liquid |
Glucose
dissolved in water |
|
|
Solid solution |
Gas |
Solid |
Solution
of hydrogen in palladium |
|
Liquid |
Solid |
Amalgam
of mercury with sodium |
|
|
Solid |
Solid |
Copper
dissolved in gold |