Rate Law and Rate
Constant
Rate law expressions
The rate of a chemical reaction at a given temperature
may depend on the concentration of one or more reactants and products.
For the chemical reaction,
![]()
where a,
b, c and d are
the stoichiometric coefficients of reactants and products.
The rate expression for this reaction is
![]()
Here exponents x and y may
or may not be equal to the stoichiometric coefficients (a and b) of the
reactants.
We can write,
![]()
where ‘k’
is called the rate constant.
Therefore,
![]()
The
equation which relates the rate of a reaction to concentration of reactants is
called rate
law or rate expression.
“Rate
law is the expression in
which reaction
rate is given in terms of molar concentration of reactants with
each term raised to some power, which may or may not be same as the stoichiometric
coefficient of the reacting species in a balanced chemical equation.”
Rate law for any reaction cannot be predicted by merely looking
at the balanced chemical equation, i.e., theoretically but must be determined experimentally.
Rate constant
Rate constant may be defined as the specific rate
of reaction when the molar concentrations of the reactants is taken to be
unity, i.e.,
![]()
Units of rate constant or specific reaction rate for a nth order reaction is
given as
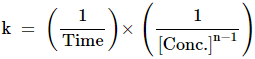
If
concentration is measured in units of mol·L−1 (abbreviated
as M), then
·
For order
(m + n), the rate constant has units of mol1−(m+n)·L(m+n)−1·s−1
·
For order
zero, the rate constant has units of mol·L−1·s−1 (or
M·s−1)
·
For order
one, the rate constant has units of s−1
·
For order
two, the rate constant has units of mol−1·L·s−1 (or
M−1·s−1)
·
For order
three, the rate constant has units of mol−2·L2·s−1 (or
M−2·s−1)
Characteristics of rate constant
i.
Greater
the value of rate constant, faster is the reaction.
ii.
Each
reaction has a particular value of rate constant at a particular temperature.
iii.
The value
of rate constant for the same reaction changes with temperature.
iv.
The value
of rate constant for a reaction doesn’t depend upon the concentration of the
reactants.
v.
Difference between Rate of Reaction and Rate
Constant :
|
S.No. |
Rate of reaction |
Reaction rate constant |
|
1 |
It is speed with which reactants are converted into
products. |
It is proportionally constant. |
|
2 |
It
is measured as the rate of decrease of concentration of reactants or the rate
of increase of concentration of products with time. |
It
is equal to the rate of reaction when the concentration of each of the reactants
in unity. |
|
3 |
It
depends upon the initial concentration of reactants |
It
is independent of the initial concentration of the reactants. It has a
constant value at fixed temperature. |