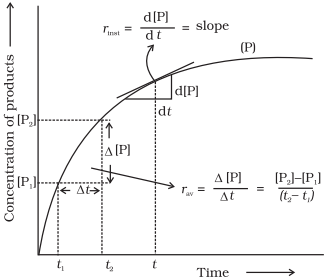
Rate of Reaction
Average rate of reaction (rav)
Rate of a
chemical reaction is the change in the concentration of any one of the
reactants or products per unit time. It is expressed in mol
L-1 s-1 or Ms-1 or atm time-1 units.
It can be expressed in terms of
i.
the rate of decrease in
concentration of any one of the reactants, or
ii.
the rate of
increase in concentration of any one of the products.
For the reaction
R → P
One mole of
the reactant R produces one mole of the product P. If [R1] and [P1]
are the concentrations of R and P respectively at time t1 and
[R2] and [P2] are their concentrations at
time t2 then,
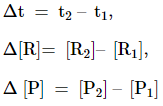
The square brackets in the above
expressions are used to express molar concentration.
Rate of disappearance of R = ![]()
Rate of appearance of P = ![]()
![]()
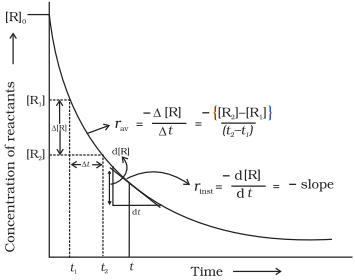
Instantaneous
rate of reaction
Rate of a
chemical reaction at a particular moment of time, is known as instantaneous
rate of reaction. It is represented by the slope of the time vs concentration curve,
![]()
or
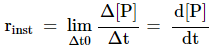
For the reaction,
![]()
![]()
Rate of disappearance of A = − ![]()
Rate of disappearance of B = − ![]()
Rate of appearance of C = ![]()
Rate of appearance of D = ![]()