Activity and Selectivity
Activity of Catalyst:
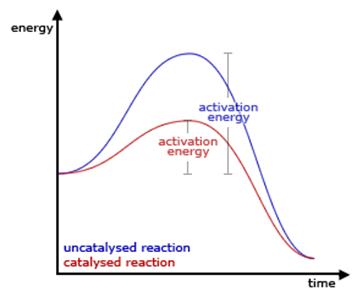
The ability of the catalyst to increase the rate
of reaction is known as the activity of the catalyst.
·
The
activity of a catalyst depends upon the strength of chemisorption to a large
extent
·
The
reactants must get adsorbed reasonably strongly on to the catalyst to become
active
·
The
hydrogenation reaction, the catalytic activity increases from Group 5 to Group
11 metals with maximum activity
Characteristics:
·
It depends upon adsorption of reactants on the surface
of catalyst. .
·
Chemisorption is the main factor governing the
activity of catalysts.
·
2H2 (g) + O2 (g) → 2H2O (l)
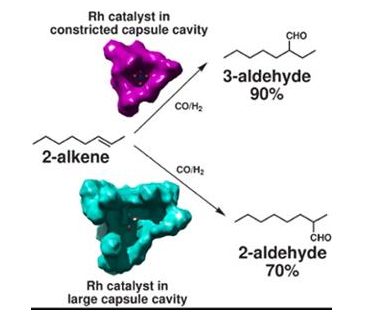
Selectivity of Catalyst:
The
selectivity of a catalyst is its ability to direct a reaction to yield a
particular product selectively.
Characteristics:
·
Selectivity
of different catalysts for same reactants is different.
·
With
different catalyst different products are obtained.
CO (g) + 3H2 (g)![]() CH4 (G) + H2o(g)
CH4 (G) + H2o(g)
Shape
Selective Catalysis by Zeolite:
The catalytic reaction that depends upon the
pore structure of the catalyst and the size of the reactant and product
molecules is called shape-selective catalysis
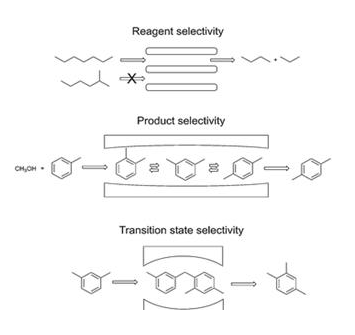
·
Zeolites are good shape-selective catalysts because of
their honeycomb-like structures.
·
They are microporous alumina silicates.
·
The reactions taking place in zeolites depend upon the
size and shape of reactant and product molecules as well as upon the pores and
cavities of the zeolites.
·
Zeolites are being very widely used as catalysts in
petrochemical industries for cracking of hydrocarbons and isomerisation.