Interhalogen Compounds
Interhalogen compounds are compounds formed
when halogen group elements react with each other. There are four types of interhalogen compounds. They are as follows:
·
XY
·
XY3
·
XY5
·
XY7
where X is halogen of larger size and X′ of smaller size and X is more electropositive than X′ . As the ratio between radii of X and X ′ increases, the number of atoms per molecule also increases. Thus, iodine (VII) fluoride should have maximum number of atoms as the ratio of radii between I and F should be maximum. That is why its formula is IF7 (having maximum number of atoms).
Preparation
The interhalogen compounds can be prepared by the direct combination or by the action of halogen on lower interhalogen compounds. The product formed depends upon some specific conditions, For example,
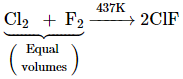
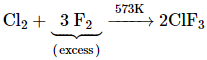
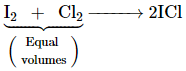
![]()
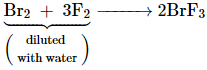
![]()
Properties
Some properties of interhalogen
compounds
|
Type |
Formula |
Physical state and colour |
Structure |
|
XX′1 |
ClF |
colourless gas |
– |
|
BrF |
pale brown gas |
– |
|
|
IFa |
detected spectroscopically |
– |
|
|
BrClb |
gas |
||
|
ICl |
ruby red solid (α-form) |
– |
|
|
Brown |
red solid (β-form) |
– |
|
|
IBr |
black solid |
– |
|
|
XX′3 |
ClF3 |
colourless gas |
Bent T-shaped |
|
BrF3 |
yellow green liquid |
Bent T-shaped |
|
|
IF3 |
yellow powder |
Bent T-shaped |
|
|
ICl3c |
orange solid |
Bent T-shaped |
|
|
XX′5 |
IF5 |
colourless gas but solid below 77 K |
Square pyramidal |
|
BrF5 |
colourless liquid |
Square pyramidal |
|
|
ClF5 |
colourless liquid |
Square pyramidal |
|
|
XX′7 |
IF7 |
colourless gas |
Pentagonal bipyramidal |
a - Very unstable; b -
The pure solid is known at room temperature; c - Dimerises
as Cl–bridged dimer (I2Cl6)
Ø These
molecules are covalent and diamagnetic in nature.
Ø The
bonds formed between these compounds are more reactive than diatomic halogen
bonds.
Ø The physical
properties of these molecules are transitional between its constituents.
Ø The
molecular structure of AX3 molecules is bent T shaped, an AX5 molecule
is square or pyramidal and the structure of AX7 is bipyramidal or pentagonal.
Ø The
bond length depends upon the size of the constituent halogens.
Ø The
molecule which consists of lighter group 17 elements is fairly colorless but one which is made up of higher halogens is
deeper in color which is due to the rise in
the molecular weight.
Uses
Ø These are
used as non-aqueous solvents.
Ø They
are used as a catalyst in few reactions.
Ø UF6 which
is used in the enrichment of 235 U is produced by using
ClF3 and BrF3.
U (s) + 3ClF3 (l) → UF6 (g)
+ 3ClF (g)
Ø These
are used as fluorinating compounds.