Sulphur and Its Compounds
Sulphur
Dioxide (SO2)
Method
of preparation of sulphur dioxide
Sulphur
dioxide is formed together with a little (6-8%) sulphur trioxide when sulphur
is burnt in air or oxygen:
S (s) + O2
(g) → SO2 (g)
In the
laboratory, it is readily generated by treating a
sulphite with dilute sulphuric acid.
SO32- (aq) + 2H+ (aq) →
H2O (l) + SO2 (g)
Industrially, it is
produced as a by-product of the roasting of sulphide ores.
4FeS2 (s)
+ 11O2 (g) → 2Fe2O3 (s) + 8 SO2 (g)
The gas
after drying is liquefied under pressure and stored in steel cylinders, because
it is a strong oxidising and reducing agent.
Physical
properties of sulphur dioxide
It is a
colourless gas with pungent smell, highly soluble in water. It liquefies at room
temperature under a pressure of two atmospheres and boils at 263 K.
Chemical
reactions of sulphur dioxide
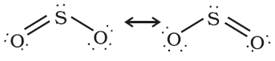
Structure
of dulphur dioxide
The molecule
of SO2 is angular. It is a resonance hybrid of the two
canonical forms:
Reaction
of sulphur dioxide with water
Sulphur
dioxide, when passed through water, forms a solution of sulphurous acid.
SO2 (g)
+ H2O (l) ⇔ H2SO3 (aq)
Reaction
of sulphur dioxide with lime water
It turns
lime water milky due to the formation of calcium sulphite.
Ca(OH)2 + SO2 →
CaSO3 (milky) + H2O
However, in
excess of SO2 milkiness disappears
due to the formation of calcium bisulphite.
CaSO3 +
SO2 + H2O → Ca(HSO3)2
Reaction
of sulphur dioxide with sodium hydroxide
It reacts readily
with sodium hydroxide solution, forming sodium sulphite, which then reacts with
more sulphur dioxide to form sodium hydrogen sulphite.
NaOH + SO2 → Na2SO3 +
H2O;
2Na2SO3 +
SO2 + H2O→ NaHSO3
Reaction
of sulphur dioxide with chlorine
Sulphur
dioxide reacts with chlorine in the presence of charcoal (which acts as a
catalyst) to give sulphuryl chloride, SO2Cl2.
SO2 (g)
+ Cl2 (g) → SO2Cl2
Reaction
of sulphur dioxide with oxygen
It is
oxidised to sulphur trioxide by oxygen in the presence of vanadium (V) oxide
catalyst.
SO2 (g)
+ O2 (g) ![]() 2SO3 (g)
2SO3 (g)
Reducing
properties of sulphur dioxide
Moist
sulphur dioxide behaves as a reducing agent. For example, it converts iron
(III) ions to iron (II) ions and decolourises acidified potassium permanganate
(VII) solution; the latter reaction is a convenient test for the gas.
2Fe3+ +
SO2 + 2H2O → 2Fe2+ + SO42- +
4H+
5SO2 +
2MnO4- + 2H2O → 5SO42- +
4H+ + 2Mn2+
Uses
of sulphur dioxide
Ø
In refining petroleum and sugar
Ø
In bleaching wool and silk and
Ø
As an anti-chlor,
disinfectant and preservative
Ø
Sulphuric acid, sodium hydrogen
sulphite and calcium hydrogen sulphite (industrial chemicals) are manufactured
from sulphur dioxide.
Ø
Liquid SO2 is
used as a solvent to dissolve a number of organic and inorganic chemicals.