Continuous Charge Distribution
We have so far dealt with charge configurations involving discrete
charges q1, q2, ...,
qn. One reason why we restrict to discrete charges is that
the mathematical treatment is simpler and does not involve calculus. For many
purposes, however, it is impractical to work in terms of discrete charges and
we need to work with continuous charge distributions. For example, on the
surface of a charged conductor, it is impractical to specify the charge
distribution in terms of the locations of the microscopic charged constituents.
It is more feasible to consider an area element ![]() †as shown in the figure. On the surface of
the conductor (which is very small on the macroscopic scale but big enough to
include a very large number of electrons) and specify the charge
†as shown in the figure. On the surface of
the conductor (which is very small on the macroscopic scale but big enough to
include a very large number of electrons) and specify the charge ![]() Q on that element.
We then define a surface charge density s at the area element by
Q on that element.
We then define a surface charge density s at the area element by
![]()
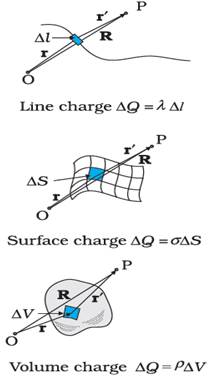
We can do this at different points on the conductor
and thus arrive at a continuous function ![]() † , called the surface charge density. The
surface charge density
† , called the surface charge density. The
surface charge density ![]() †so defined ignores the quantisation
of charge and the discontinuity in charge distribution at the microscopic
level. At the microscopic level, charge distribution is discontinuous,
because they are discrete charges separated by intervening space where there is
no charge.
†so defined ignores the quantisation
of charge and the discontinuity in charge distribution at the microscopic
level. At the microscopic level, charge distribution is discontinuous,
because they are discrete charges separated by intervening space where there is
no charge. ![]() †represents
macroscopic surface charge density, which in a sense, is a smoothed out average
of the microscopic charge density over an area element
†represents
macroscopic surface charge density, which in a sense, is a smoothed out average
of the microscopic charge density over an area element ![]() S which,
as said before, is large microscopically but small macroscopically. The units
for
S which,
as said before, is large microscopically but small macroscopically. The units
for ![]() †are C/m2.
†are C/m2.
Similar considerations apply for a line charge
distribution and a volume charge distribution. The linear charge density ![]() †of a wire is defined by
†of a wire is defined by
![]()
where ![]() †is a small line element of wire on the
macroscopic scale that, however, includes a large number of microscopic charged
constituents, and
†is a small line element of wire on the
macroscopic scale that, however, includes a large number of microscopic charged
constituents, and ![]() †is the charge contained in that line element.
The unit for
†is the charge contained in that line element.
The unit for ![]() †is C/m. The volume charge density (sometimes
simply called charge density) is defined in a similar manner:
†is C/m. The volume charge density (sometimes
simply called charge density) is defined in a similar manner:
![]()
where ![]() Q is the charge
included in the macroscopically small volume element
Q is the charge
included in the macroscopically small volume element ![]() V that includes a
large number of microscopic charged constituents. The units for
V that includes a
large number of microscopic charged constituents. The units for ![]() † are C/m3.
† are C/m3.
The notion of continuous charge distribution is similar to that we
adopt for continuous mass distribution in mechanics. When we refer to the
density of a liquid, we are referring to its macroscopic density. We regard it
as a continuous fluid and ignore its discrete molecular constitution. The field
due to a continuous charge distribution can be obtained in much the same way as
for a system of discrete charges. Suppose a continuous charge distribution in
space has a charge density![]() †. Choose any convenient origin O and let the
position vector of any point in the charge distribution be r. The charge density r may vary from point to point, i.e., it is a
function of r. Divide the charge distribution into small volume elements of
size
†. Choose any convenient origin O and let the
position vector of any point in the charge distribution be r. The charge density r may vary from point to point, i.e., it is a
function of r. Divide the charge distribution into small volume elements of
size ![]() V. The charge in a
volume element
V. The charge in a
volume element ![]() V is
V is ![]() V.
V.
Now, consider any general point P (inside or outside the
distribution) with position vector R as shown in the figure. Electric field due
to the charge ![]() V is given by
Coulombís law:
V is given by
Coulombís law:
![]() †
†![]() †
†
where ![]() †is the distance between the charge element and
P and
†is the distance between the charge element and
P and![]() †is a unit vector in the direction from the
charge element to P. By the superposition principle, the total electric field
due to the charge distribution is obtained by summing over electric fields due
to different volume elements:
†is a unit vector in the direction from the
charge element to P. By the superposition principle, the total electric field
due to the charge distribution is obtained by summing over electric fields due
to different volume elements:
![]() †
†
Note that ![]() †all can vary from point to point. In a strict
mathematical method, we should let
†all can vary from point to point. In a strict
mathematical method, we should let ![]() †and the sum then becomes an integral; but we
omit that discussion here, for simplicity. In short, using Coulombís law and
the superposition principle, electric field can be determined for any charge
distribution, discrete or continuous or part discrete and part continuous.
†and the sum then becomes an integral; but we
omit that discussion here, for simplicity. In short, using Coulombís law and
the superposition principle, electric field can be determined for any charge
distribution, discrete or continuous or part discrete and part continuous.