Carbon Resistors
Resistors are used to resist or control the
flow of electrons by the conductive material. They do not provide any power to
the circuit. They may reduce the voltage and current passing through the
circuit. Hence resistors are passive devices.

There are many materials used to produce
resistance particularly metals and alloys like Nichrome,
brass, platinum and tungsten alloys. However, most of these metals have low
electrical resistivity, unlike carbon resistor, which makes it difficult to
produce high resistances without becoming bulky [Resistance ∝ {Length
×Resistivity}]. However, they can produce highly accurate values of resistance
and hence are used usually to calibrate and compare resistances.
For most practical purposes, however, carbon
resistors are preferred. This is because they are cheap to produce, compact and
can be directly printed onto circuit boards (like the computer processors in
phones and tablets). They also reproduce resistance fairly well within
practical requirements. Compared to metal wires which are expensive to produce,
carbon is abundantly available making it cheap.
Uses of Carbon Resistors
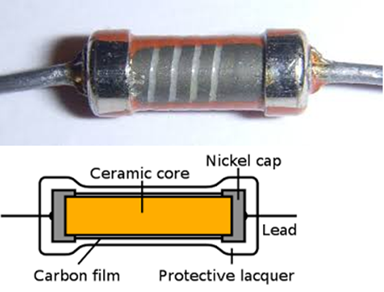
The carbon resistor contains carbon coated onto
a ceramic core. A spiral is etched on the deposited carbon which turns it into
a wire wound on a ceramic core. Depending on the resistance required, pitch,
diameter and length of the carbon spiral vary. Nickel caps are attached to both
ends of the core so as to create a good contact between the carbon and lead.
The leads are soldered onto the nickel caps and the entire resistor is coated
with lacquer for electrical insulation.
For small resistances required for small
currents, the metal caps act as heat sinks to carry away heat dissipated by the
resistor. For larger current requirements, a metal heat sink is separately
attached to carry away excess heat and to prevent the resistor from burning up.
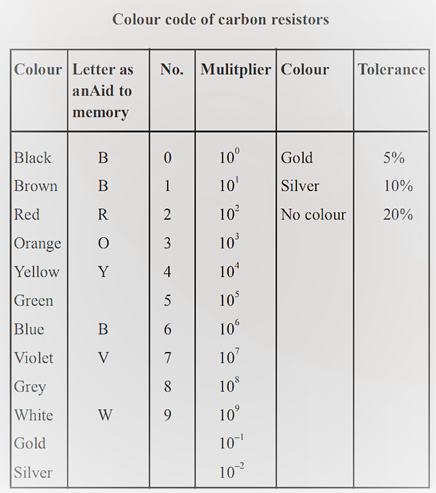
Colour Code of Carbon resistors
Carbon resistors are specially colour-coded to
identify the resistance.
To
remember the value of colour coding used for carbon resistor, the following
sentences are found to be of great help (where bold letters stand for colours).
B B ROY Green, Britain Very Good Wife Gold
Silver.
Way of finding the resistance of carbon resistor from its colour coding
In
the system of colour coding, Strips of different colours are given on the body
of the resistor, figure. The colours on strips are noted from left to right.

Ř Colour of the first stip
A
from the end indicates the first significant figure of resistance in ohm
Ř Colour of the second strip B
indicate the second significant figure of resistance in ohm.
Ř The colour of the
third strip C indicates the multiplier, i.e., the number of
zeros that will follow after the two significant figure.
Ř The colour of
fourth strip R indicates the tolerance limit of the resistance
value of percentage accuracy of resistance.