Drift
Velocity and Mobility
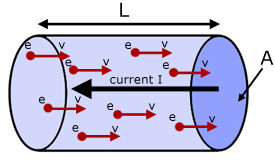
Drift Velocity
“Drift
velocity is defined as the average velocity with which the free electrons get
drifted towards the positive end of the conductor under the influence of an
external electric field applied”.
The drift velocity of electrons
is of the order of ![]() m/s .
m/s .
If V is the potential
difference applied across the ends of the conductor of length l, the magnitude
of electric field set up is
![]()
Each free electrons in the
conductor experience a force,
![]() .
.
The acceleration of each
electron is ![]()
Average Drift Velocity,
![]() as (v=at)
as (v=at)
where, τ is the
relaxation time
Relation between Drift Velocity and
Current
Drift
velocity:-The velocity with which the free electrons
are drifted towards the positive terminal, under the action of the applied
field, is called the drift velocity of the free electrons.
V
= (eV/ml)![]()
Here,
e is the charge of electron, V is the potential difference, m is the mass
and ![]() is the relaxation time.
is the relaxation time.
Electric
current and Drift velocity:- I= q/t = nAve
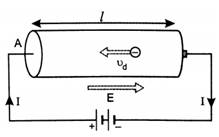
Consider a conductor (say a
copper wire) of length l and of
uniform area of cross-section
Volume of the conductor = A ×
l.
If n is the number density of electrons, i.e., the number of free
electrons per unit volume of the conductor, then total number of free electrons
in the conductor
= A ×
l × n.
Then total charge on all the
free electrons in the conductor,
q = A × l × n × e
The electric field set up
across the conductor is given by E = ![]() (in magnitude)
(in magnitude)
5. Due to this field, the free
electrons present in the conductor will begin to move with a drift velocity vd towards the left hand side as
shown in figure
Time taken by the free
electrons to cross the conductors,
![]()
hence,
Current
![]()
![]()
Therefore, ![]()
Putting value of ![]() ,
we have
,
we have
![]()
Relaxation Time (τ)
The
time interval between two successive collisions of electrons with the positive
ions in the metallic lattice is defined as relaxation time
![]()
Mobility
Drift velocity per unit
electric field is called mobility of electron i.e.
![]()
Mobility of charge carrier (µ),
responsible for current is defined as the magnitude of drift velocity of charge
per unit electric filed applied, i.e.,
![]()
![]()
![]()
Therefore, Mobility of electrons
![]()