Electrical Energy and Power
The law of conservation states that - Energy
can neither be created nor be destroyed. It can only be transformed from one
form to another. There are mainly two types of energy. They are Kinetic
Energy and Potential Energy. The light energy, electrical energy,
mechanical energy, all these forms of energy are either kinetic or potential.
So electrical energy is one of the many forms of energy.
As the law mentions, we can say that electrical
energy can be produced from other forms of energy and also the electrical
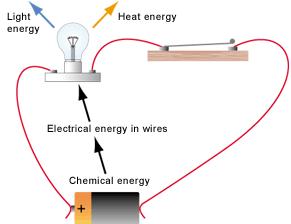
energy can be transformed to other forms of energy. When an electric bulb is
connected to the circuit, chemical energy in cell is converted into electrical
energy but not anywhere in the circuit. Then the electrical energy is converted
or transformed mainly into light energy and heat energy. In heaters, electrical
energy is converted into heat energy. Lightning is the example of electrical
energy in nature.
Electrical
energy conversion
The capacity of doing work is
called Energy. In an electric field the energy that is stored in the
charged particles is called Electrical Energy.
All things in this universe are made of atoms.
Each atom has a nucleus which is surrounded by electrons and the electrons revolve
around the atoms. Metals like copper can easily leave their orbits and they are
called as Conductors. When the electron escapes from its orbit the
electrons moves near the nucleus of another atom. The electric current is
produced by the flow of these electrons.
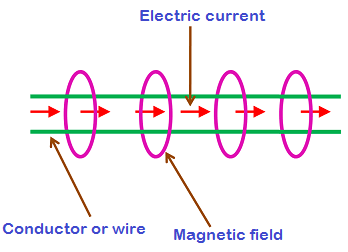
Now consider a magnet. A magnet has two poles,
a North and South Pole. When two magnets are brought to each other they either
attract or repel each other. The magnetic field between the magnets is the one
which brings them to move. This magnetic field has an effect on electrons. When
a magnet is placed near a conductor like copper, the magnetic field attracts or
repels the electrons. This movement of electrons is the electricity.
Electricity
and magnetism
Production of Electrical Energy
Electricity is generated from the huge
generating units that are placed in the hydro electric power stations. The
principle of these generators is the same as we can see with the magnet and the
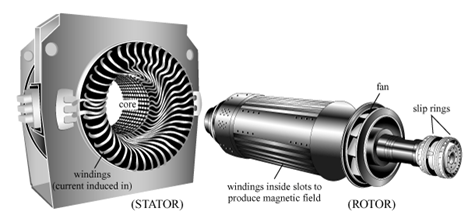
copper wire. The rotor and the stator are the two main components of a
generator. The rotor consists of a number of magnets. The stator consists of a
series of copper bars.
W
= Vq = V(It)
Unit
of electric energy:-
1
joule = 1 watt sec
1
kilowatt hour = 1000 watt hour
When a magnet is rotated beside the copper bar,
the movement of electrons occurs due to the presence of the magnetic field and
thus electricity is produced. Likewise the rotor has the same effect as that of
the magnet. The rotor is made up of electro magnets. The electro magnets are
used when we need a very powerful magnet. It consists of a metal core which is
placed inside the coil of electric wire.
Rotor
and Stator
When the current flows through the electric
coil, there occurs a magnetic field. It is able to control the force of
magnetism of these electro magnets. As the rotor has many electromagnets they
attract and repel the electrons which are present in the copper bars
alternatively. Thus the generator generates electricity. It is the mechanical
force of water which makes the rotor rotate. When the water hits the blades of
the turbine it rotates. This rotating motion of turbine will then drive the
shaft which is attached to the rotor. So when the rotor rotates around the
stator, the movement of electrons take place.
Consider a circuit with a cell and a resistor.
The terminal voltage of the cell is V
and the resistance is R. Let us
imagine that the total charge of electrons is Q. So the work done to move the charge Q through the potential difference V is the product of the potential energy and the charge which has
moved across the potential energy.
W = Q V
We know that the charge Q = current ◊ time = I t.
So ††††††††††††††††† W = V I t
We know that by ohmís law,
Voltage = current ◊ resistance = I R, Substituting in the equation
W = (IR) I t
= I2 R t
Current = ![]() †=
†= ![]() †
†
Thus †††††††††††††††††††††††† W
= ![]() †R t
†R t
= ![]() t
t
The unit of energy or work is joule.
Power
Power can be defined as the work done per unit
time. Electrical power is the rate of energy consumed in a circuit.
P = ![]() †
†
= ![]() †/t
†/t
Here V is the voltage, Q is the charge and t is the time in seconds.
We know that ![]() †= I,
the current.
†= I,
the current.
So substituting we get P = V I
(a)
P = VI
(b)
P = I2R = V2/R
Unit
of power:-1 watt = 1 volt ◊ 1 amp
Consider that the voltage is like the speed at
which a car is being driven in a road. The number of cars that passes a mile
stone on the road can be compared to the current. So power can be compared as
the capacity of the road that can handle the number of cars. The energy
consumed can be compared to the number of cars that has driven on the road in
an hour.
We know that voltage V = IR
So ††††††††††††††††† W = (IR)
I t
= I2 R t
So ††††††††††††††††† P = I2 R t /t
= I2 R.
We know that I = ![]()
Thus †††††††††††† W = ![]() †R t
†R t
= ![]() t
t
P = ![]() †
†
= ![]()
The unit of power is joule / second or watt.
The electric power can be supplied by electric
batteries, electric generators etc. Based on electric power, the components of
an electric circuit is divided into two. They are passive devices and
active devices. Passive devices do not require an
external source. They consume electric power within the circuit and then
converts into other forms of energy like heat energy, light energy etc.
Electric heaters and light bulbs are examples for passive devices. They do not
perform function like amplification, oscillation and generation.
In active devices forms of energy like chemical
energy, mechanical energy is converted into electric potential energy. Electric
generators and batteries are example for this. They produce energy in the form
of voltage or current.