Interference of Light
Superposition
of two waves, travelling through the same medium, is called interference.
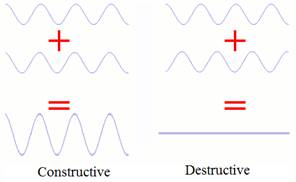
Constructive
interference occurs when the two interfering waves have
a displacement in the same direction and the amplitude of the resulting wave is
the addition of amplitudes of interfering waves.
Destructive
interference occurs when the two interfering waves have
a displacement in different direction (out of phase) and the amplitude of the
resulting wave is the difference of amplitudes of interfering waves.
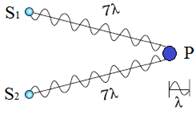
Consider
two coherent sources S1 and
S2 a
point P for which S1P
= S2P.
Since the distances S1P
and S2P
are equal, waves from S1 and
S2 will
take the same time to travel to the point P and waves that originate from S1 and
S2 in
phase will also arrive, at the point P, in phase.
If the
displacement produced by the source S1 at
the point P is given by
y1 = a
cos ωt
then, the
displacement produced by the source S2 (at
the point P) will also be given by
y2 = a
cos ωt
Thus,
the resultant of displacement at P would be given by
y = y1 + y2 = 2
a cos ωt
Since
the intensity is the proportional to the square of the amplitude, the resultant
intensity will be given by,
I = 4Io
where Io represents
the intensity produced by each one of the individual sources; Io is
proportional to a2.
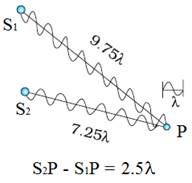
In fact
for all points where the phase difference is 2nπ or path difference is nλ, the interference will be constructive.
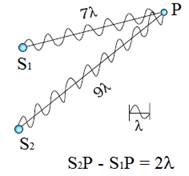
If the
phase difference is (2n + 1)π or path
difference is 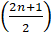 λ, the interference will be
destructive.
λ, the interference will be
destructive.
For any
other arbitrary point let the phase difference between the two displacements be
φ.
y1 = a
cos ωt
y2 = a cos
(ωt + φ)
The
resultant displacement will be given by
y = y1 + y2 = a
[cos ωt + cos (ωt + φ]
![]()
Since φ is constant, the
amplitude of the resultant displacement is 2a cos ![]() .
.
Or the intensity I = 4Io cos2 ![]()
If the two sources are not coherent the average intensity
will be given by
<I> = 4Io <cos2 ![]() >
>
where angular brackets represent time averaging.
The function cos2 ![]() will randomly vary between 0 and 1 and the average
value will be
will randomly vary between 0 and 1 and the average
value will be ![]() .
.
The resultant intensity will be given by,
I = 2Io