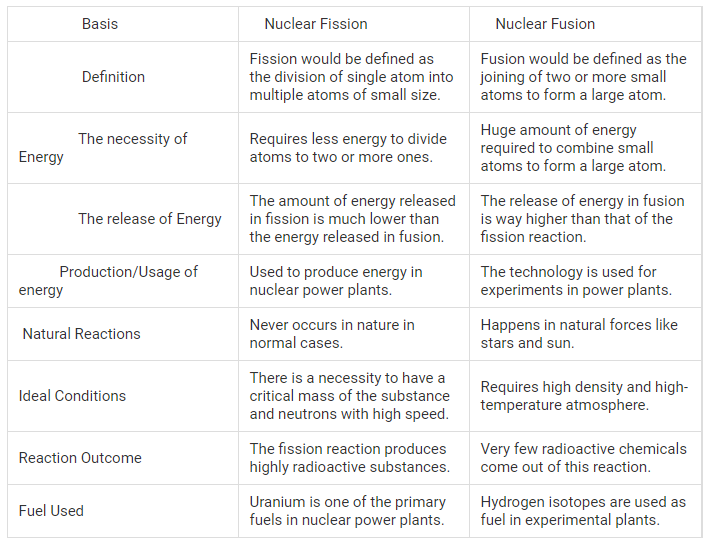
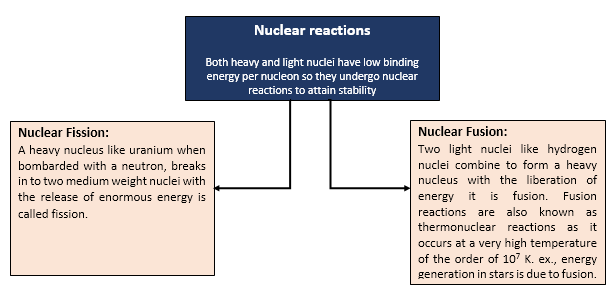
Nuclear Fission and Fusion
Nuclear Fission
The
process of splitting of a heavy nucleus into two nuclei of nearly comparable
masses with liberation of energy is called nuclear fission.
![]() +
+ ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() +
+ ![]() + 3
+ 3![]() + Q
+ Q
Neutron reproduction
factor is defined as the ratio of the rate of production of neutrons to the
rate of loss of neutrons. Thus,
![]()
A fission
reaction will be steady, in case k = 1. In case k > 1, the fission reaction
will accelerate and it will retard, in case k < 1.
Nuclear Reactor
Main parts and their functions:
Fuel:
It is a
fissionable material mostly U-235.
Moderator:
It is
used to slow down the neutrons released during the fission. The most common
moderators are water, heavy water and graphite.
Control Rods:
These
rods are cadmium or boron, which control the chain reaction by absorbing
neutrons.
Coolant and Heat Exchange:
The
coolant takes away heat from the reactor core and in turn heats the water in
the heat exchanger to produce steam. The commonly used coolants are liquid
sodium and heavy water.
Radiation Shielding:
These are
thick concrete walls, which stop the radiations from going out.
Nuclear Fusion
It is the process in which
two or more small nuclei fuse together to form a single heavy nucleus.
The mass of the single
heavy nucleus formed is less than the total initial mass of the mass of the
parent nuclei.
This difference in mass
appears in the form of energy (as per, E = mc2).
Example: 1H2 + 1H2 → 2He4 +
Enormous amount of energy
Enormous amount of energy
produced by the sun is due to the phenomenon of nuclear fusion.
 s
s