Physical Properties
Ø Alkanes are almost non-polar molecules because of the covalent nature of C-C and C-H bonds and due to very little difference of electronegativity between carbon and hydrogen atoms.
Ø They possess weak van der Waals forces.
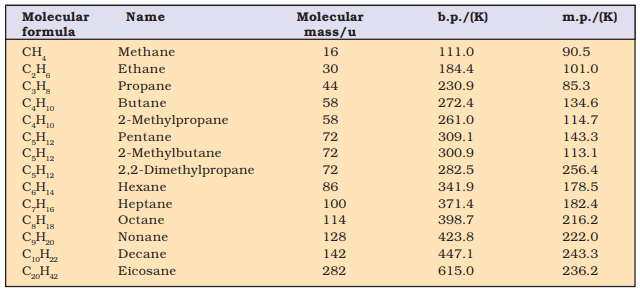
Ø Due to the weak forces, the first four members, C1 to C4 are gases, C5 to C17 are liquids and those containing 18 carbon atoms or more are solids at 298 K.
Ø They are colourless and odourless.
Petrol is a mixture of hydrocarbons and is used as a fuel for automobiles. Petrol and lower fractions of petroleum are also used for dry cleaning of clothes to remove grease stains. Grease (mixture of higher alkanes) is non-polar and, hence, hydrophobic in nature.
It is generally observed that in relation to solubility of substances in solvents, polar substances are soluble in polar solvents, whereas the non-polar ones in non-polar solvents i.e., like dissolves like.
Boiling point (b.p.) of different alkanes are given in below table from which it is clear that there is a steady increase in boiling point with increase in molecular mass. This is due to the fact that the intermolecular van der Waals forces increase with increase of the molecular size or the surface area of the molecule.
Variation of Melting Point and Boiling
Point in Alkanes