Hardness of Water
Types of Water:
There are two types of water. They are:
1.
Hard
water
2.
Soft
water
1. Hard Water:
Presence of calcium and magnesium salts in the form of
hydrogen carbonate, chloride and sulphate in water makes water ‘hard’.
·
Hard
water does not give lather with soap.
·
Hard
water forms precipitate with soap.
2. Soft Water:
Water free from
soluble salts of calcium and magnesium is called Soft water.
·
It gives lather with soap easily.
·
Because
soft water has few calcium ions, there is no inhibition of the lathering action
of soaps.
Hardness of Water:
The hardness of water is of two types:
a) Temporary hardness and
b) Permanent hardness.
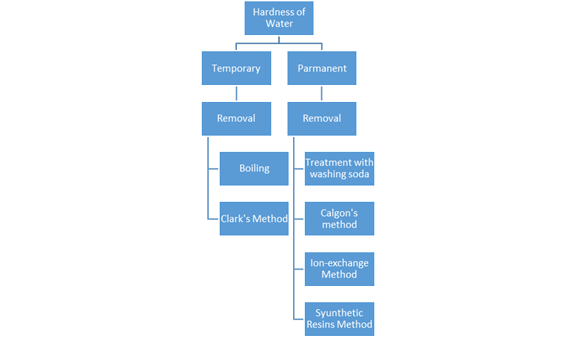
a) Temporary Hardness:
Temporary hardness is due to the presence of magnesium
and calcium hydrogen carbonates. It can be removed by:
·
Boiling:
During boiling, the
soluble Mg(HCO3)2 is converted into insoluble Mg(OH)2
and Ca(HCO3)2 is changed to insoluble CaCO3.
Thus Mg(OH)2 is precipitated. These precipitates can be removed by
filtration. Filtrate thus obtained will be soft water.
|
Mg(HCO3)2 |
|
Mg(OH)2 |
|
Ca(HCO3)2 |
|
CaCO3 |
·
Clark’s Method :
In this method
calculated amount of lime is added to hard water. It precipitates out calcium
carbonate and magnesium hydroxide which can be filtered off.
|
Ca(HCO3)2
+ Ca(OH)2 |
|
2CaCO3 |
|
Mg(HCO3)2
+ 2CaCO3 |
|
2CaCO3+Mg(OH)2 |
b) Permanent Hardness:
It is due to the presence of soluble salts of
magnesium and calcium in the form of chlorides and sulphates in water.
Permanent hardness is not removed by boiling. It can be removed by the
following methods:
·
Treatment with Washing Soda (sodium
carbonate):
Washing soda reacts with soluble calcium and magnesium
chlorides and sulphates in hard water to form insoluble carbonates.
|
MCl2 + Na2CO3 |
|
MCO3
|
|
MSO4 + Na2CO3 |
|
MCO3
|
·
Calgon’s Method:
Sodium
hexametaphosphate (Na6P6O18) commercially
called ‘calgon’. When it is added to hard water, the following reactions take
place:
|
Na6P6O16 |
|
2Na
+ (Na4P6O18)2- (M = Mg, Ca) |
|
M2+ + (Na4P6O18)2- |
|
(Na2MP6O18)2-
+ 2Na+ |
The complex anion keeps the Mg2+ and
Ca2+ ions in solution.
·
Ion-exchange Method:
This method is also called zeolite or permutit process. Hydrated sodium aluminium silicate is
known as zeolite or permutit. For the sake of simplicity, sodium aluminium
silicate (NaAlSiO4) can be written as NaZ. When this is added in
hard water, exchange reactions take place.
|
2NaZ (s) + M2+ (aq)
|
·
Synthetic Resins Method:
This method is more
efficient than zeolite process. Cation exchange resins contain large organic
molecule with - SO3H group and are water insoluble. Ion exchange
resin (RSO3H) is changed to RNa by treating it with NaCl. The resin
exchanges Na+ ions with Ca2+ and Mg2+ ions present in
hard water to make the water soft. Here R is resin anion.
|
2RNa
(s) + M2+ (aq) |
Heavy Water (D2O):
It is extensively
used as a moderator in nuclear reactors and in exchange reactions for the study
of reaction mechanisms. It can be prepared by exhaustive electrolysis of water
or as a by-product in some fertilizer industries. It is used for the
preparation of other deuterium compounds.
For example,
|
CaC2 + 2D2O |
|
C2D2
+ Ca(OD)2 |
|
SO3
+ D2O |
|
D2SO4 |
|
Al2C3
+ 12D2O |
|
3CD4 + 4Al(OD)3 |