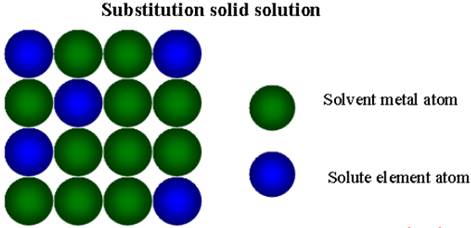
Solid Solutions
Solid
solution is a solid-state solution of one or more solutes in a solvent. Such a
multi-component system is considered a solution rather than a compound when the
crystal structure of the solvent remains unchanged by addition of the solutes,
and when the chemical components remain in a single homogeneous phase. This
often happens when the two elements (generally metals) involved are close
together on the periodic table; conversely, a chemical compound generally results
when two metals involved are not near each other on the periodic table.
The
solid solution needs to be distinguished from mechanical mixtures of powdered
solids like two salts, sugar and salt, etc. The mechanical mixtures have total
or partial miscibility gap in solid state. Examples of solid solutions include
crystallized salts from their liquid mixture, metal alloys, moist
solids. In the case of metal alloys intermetallic compounds occur frequently.