Preparation of Colloids
Chemical
methods:
Colloidal
solutions can be prepared by chemical reactions which form molecules by double
displacement, oxidation, reduction or hydrolysis. These molecules then
aggregate to form sols.
As2O3 +
3H2S → As2S3 (sol)
+ 3H2O
SO2 +
2H2S → 3S (sol) + 2H2O
2AuCl3 +
3 HCHO + 3H2O → 2Au (sol) + 3HCOOH + 6HCl
FeCl3 +
3H2O → Fe (OH)3 (sol)
+ 3HCl
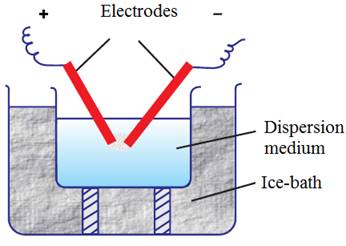
Electrical
disintegration or Bredig’s arc method:
This process
involves dispersion as well as condensation. Colloidal sols of metals such as
gold, silver, platinum, etc., can be prepared by this method. In this method,
electric arc is struck between electrodes of the metal immersed in the
dispersion medium. The intense heat produced vapourises
the metal, which then condenses to form particles of colloidal size.
Peptization:
Peptization is defined
as the process of converting a precipitate into colloidal
sol by shaking it with dispersion medium in the presence of a small
amount of electrolyte. The electrolyte used for this purpose is
called peptizing agent.
During peptization, the precipitate adsorbs one
of the ions of the electrolyte on its surface. This causes the development
of positive or negative charge on precipitates, which
ultimately break up into smaller particles of the size of a
colloid.