Properties of
Colloidal Solutions
Heterogeneous nature:
Colloidal sols are heterogeneous in nature. They consist of two phases;
the dispersed phase and the dispersion medium.
Stable nature:
The colloidal solutions are quite stable. Their particles are in a state
of motion and do not settle down at the bottom of the container.
Stability of sols:
Sols are thermodynamically unstable and the dispersed phase (colloidal
particles), tend to separate out on long standing due to the van der
Waal's attraction forces. However sols tend to exhibit some stability due
to
a)
Stronger
repulsive forces between the similarly charged particles
b)
Particle-solvent
interactions: Due to strong particle-solvent (dispersion medium)
interactions, the colloidal particles get strongly solvated.
Filterability:
Colloidal particles are readily passed through the ordinary filter
papers. However they can be retained by special filters known as ultra-filters
(parchment paper).
Colligative properties:
Due to formation of bigger aggregates, the number of particles in a
colloidal solution is comparatively small as compared to a true solution.
Hence, the values of colligative properties (osmotic pressure,
lowering in vapour pressure, depression in freezing
point and elevation in boiling point) are of smaller as
compared to values shown by true solutions at same
concentrations.
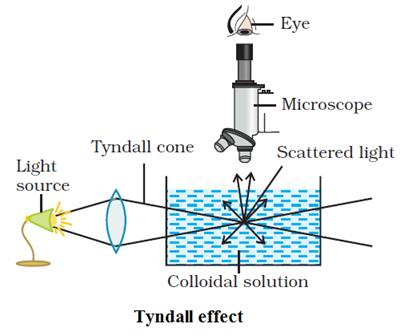
Tyndall effect:
The property of colloids by virtue of which path of a beam of light is
illuminated, is called Tyndall effect. The Tyndall effect is
due to the fact that colloidal particles scatter light in all directions in
space. This scattering of light illuminates the path of beam in the colloidal
dispersion.
Tyndall
effect is observed only when,
a)
The
diameter of the dispersed particles is not much smaller than the wavelength of
the light used; and
b)
The
refractive indices of the dispersed phase and the dispersion medium differ
greatly in magnitude.
Colour:
The colour of colloidal solution depends on the wavelength of light
scattered by the dispersed particles, size and nature of the particles and the
manner which the observer receives the light. For example, a mixture of milk
and water appears blue when viewed by the reflected light and red when viewed
by the transmitted light. Finest gold sol is red in colour; as the size of
particles increases, it appears purple, then blue and finally golden.
Brownian movement:
The colloidal particles are moving at random in a zig–zag motion.
This type of motion is called Brownian movement.
The molecules of the dispersion medium are constantly colloiding with the particles of the dispersed phase. The
impacts of the dispersion medium particles are unequal, thus causing a zig-zag motion
of the dispersed phase particles.
The Brownian movement helps in providing stability to colloidal sols by
not allowing them to settle down.
Diffusion:
The sol particles diffuse from higher concentration to lower
concentration region. However, due to bigger size, they diffuse at a lesser
speed.
Sedimentation:
The colloidal particles settle down under the influence of gravity at a
very slow rate. This phenomenon is used for determining the molecular mass of
the macromolecules.
Electrical Properties
Charge on colloidal particles:
Colloidal particles always carry an electric charge. The nature of this
charge is the same on all the particles in a given colloidal solution and may
be either positive or negative.
The charge on the sol particles is due to one or more reasons, viz., due
to electron capture by sol particles during electro-dispersion of metals, due
to preferential adsorption of ions from solution and/or due to formulation of
electrical double layer.
Electrophoresis:
Ø The phenomenon of movement of colloidal
particles under an applied electric field is called electrophoresis.
Ø If the sol particles accumulate near the
negative electrode, the charge on the particles is positive.
Ø If the sol particles accumulate near the
positive electrode, the charge on the particles is negative.
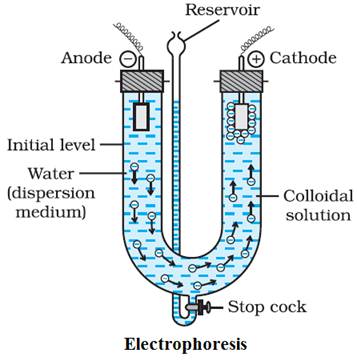
Ø When electrophoresis of a sol is carried out
without stirring, the bottom layer gradually becomes more concentrated while
the top layer which contains pure solution may be decanted.
Ø The process of transferring the clear liquid
without disturbing the sediments is called decantation.
Ø This is called electro-decanation and is used for the purification as
well as for concentrating the sol.
Ø The reverse of electrophoresis is
called sedimentation potential or Dorn effect. The
sedimentation potential is setup when a particle is forced to move in a resting
liquid.
Electrical double layer theory
The electrical properties of colloids can be explained by electrical
double layer theory. According to this theory a double layer of
ions appear at the surface of solid.
Example
1: When silver nitrate solution is added to potassium
iodide solution, the precipitated silver iodide adsorbs iodide ions
from the dispersion medium and negatively charged colloidal solution results.
AgI/I– (Negatively
charged)
However
when KI solution is added to AgNO3 solution,
positively charged sol results due to adsorption of Ag+ ions
from dispersion medium.
AgI/Ag+ (Positively
charged)
Example
2: If FeCl3 is added to excess of hot water, a positively
charged sol of hydrated ferric oxide is formed due to adsorption of Fe3+ ions.
Fe2O3.xH2O/Fe3+
However,
when ferric chloride is added to NaOH a negatively
charged sol is obtained with adsorption of OH- ions.
Fe2O3.xH2O/OH–
Having
acquired a positive or a negative charge by selective adsorption on the surface
of a colloidal particle as stated above, this layer attracts counter ions from
the medium forming a second layer, e.g.,
AgI/I-K+ or
AgI/Ag+I-
The ion
preferentially adsorbed is held in fixed part and imparts charge to colloidal
particles.
The
second part consists of a diffuse mobile layer of ions. This second layer
consists of both the type of charges. The net charge on the second layer is
exactly equal to that on the fixed part.
The
existence of opposite sign on fixed and diffused parts of double layer leads to
appearance of a difference of potential, known as zeta potential or electrokinetic potential.
When
electric field is employed the particles move (electrophoresis).