Phase
ü The
quantity ![]() δ)
is called the phase.
δ)
is called the phase.
ü It
determines the status of the particle in simple harmonic motion.
ü If
the phase is zero at a certain instant,![]() δ)
= 0 and
δ)
= 0 and ![]() = A
= A ![]() ,
which means that the particle is crossing the mean position and is going
towards the positive direction.
,
which means that the particle is crossing the mean position and is going
towards the positive direction.
ü If
the phase is n/2, we get x = A, v = 0 so that the particle is at the positive
extreme position.
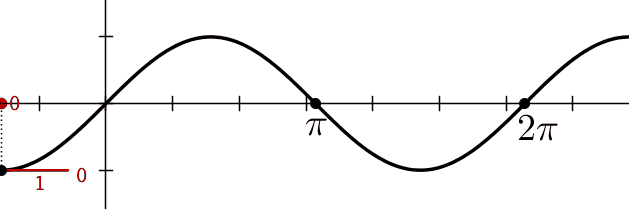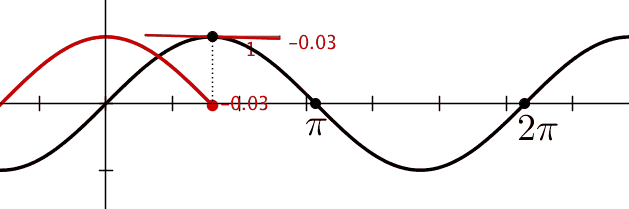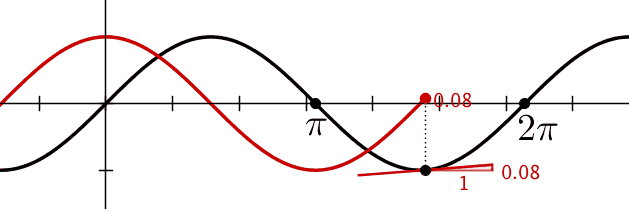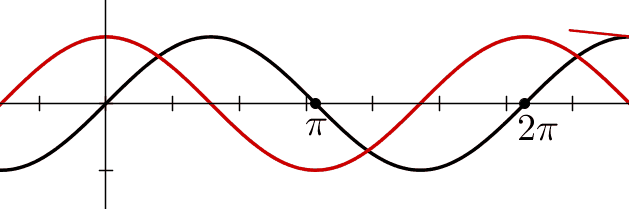
Figure shows graphically the
variation of position and velocity as a function of the phase.
Phase constant
ü The
constant ![]() appearing in equation is called the phase
constant.
appearing in equation is called the phase
constant.
ü This
constant depends on the choice of the instant t = 0.
ü To
describe the motion quantitatively, a particular instant should be called t = 0
and measurement of time should be made from this instant.
ü This
instant may be chosen according to the convenience of the problem.