Variation of g with Depth
Effect of Depth on g:
Consider the earth to be a sphere of mass M, radius R and centre O. The
acceleration due to gravity at any point A
on the surface of the earth will be
g = ![]()
Assuming the earth to be a homogeneous sphere
of average density ![]() , then its
total mass will be
, then its
total mass will be
M = Volume × density
= 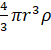
g = 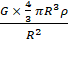
g = 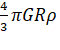
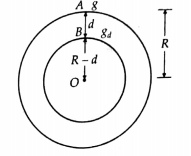
Effect of depth on g
Let ![]() be the acceleration due to gravity at a point B at depth d below the surface of the earth.
A body at B is situated at the surface of inner solid sphere and lies inside
the spherical shell of thickness d.
The gravitational force of attraction on a body inside a spherical shell is
always zero. Therefore, a body at B
experiences gravitational force due to inner shaded sphere of radius (R − d) and mass M', where
be the acceleration due to gravity at a point B at depth d below the surface of the earth.
A body at B is situated at the surface of inner solid sphere and lies inside
the spherical shell of thickness d.
The gravitational force of attraction on a body inside a spherical shell is
always zero. Therefore, a body at B
experiences gravitational force due to inner shaded sphere of radius (R − d) and mass M', where
![]() =
= 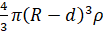
![]() =
= ![]()
= 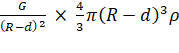
![]() =
= 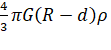
![]() =
= 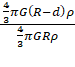
= ![]()
= ![]()
![]() =
= 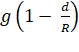
Clearly, the acceleration due to gravity decreases with the
increase in depth d. That is why the
acceleration due to gravity is less in mines than that on earth's surface.
Relation between Height h
and Depth d for the Same Change in g:
Acceleration due to gravity at a height
h above the earth's surface,
![]() =
= 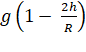
Acceleration due to gravity at a depth d
below the earth's surface,
![]() =
= 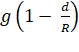
For the same change in g, we have
![]() =
= ![]()
∴ 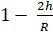 =
= 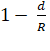 or
or 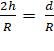 or
or ![]()
Hence the acceleration due to gravity
at a height h above the earth's surface will be same as that at depth d = ![]() , below the
earth's surface. But this fact holds only when
, below the
earth's surface. But this fact holds only when ![]() .
.